Global Sanitation Fund Programme Nepal
GLOBAL SANITATION FUND PROGRAMME
The Global Sanitation Fund (GSF) is a pooled global
fund to boost expenditure on sanitation and hygiene to help large number
of poor people to attain safe sanitation services and adopt good
hygiene practices. It is estimated that 2.5 billion people, about 40% of
the world population, do not have access to basic sanitation. The GSF
offers an efficient and cost-effective opportunity for
contributors to help the world’s poorest people access this most
basic everyday need. The GSF is a program of the Water Supply and
Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) and was launched in 2008.
GLOBAL SANITATION FUND PROGRAMME NEPAL
GSF in Nepal started from 2010 for five years with the
commitment to support the government for operationalization
of Sanitation and Hygiene Master Plan 2011. The successful ongoing
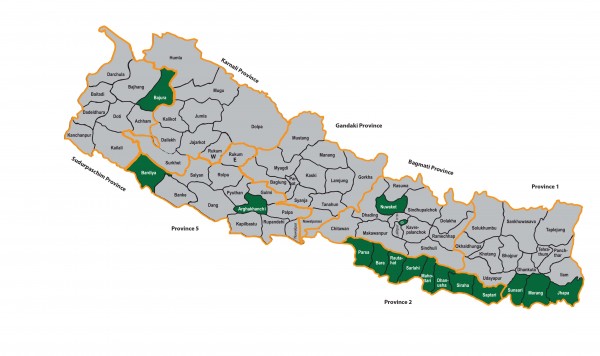
implementation of GSF Program in Nepal in Six districts (Bajura, Bardiya,
Arghakhanchi, Sindhupalchowk, Sunsari and Bhaktapur ) and six
muncipilities ( Madhyapur Thimi, Gulariya, Tikapur, Bhaktapur, Ithari and
Inaruwa ) in five developmental regions, has led towards expansion of
the program in 8 Terai districts (Parsa, Bara, Rautahat,
Sarlahi, Mahottari, Dhanusha,Siraha and Saptari) and 1 mountain
district Dolakha covering the time-frame up to 2017. In 2015, GSF was further
expanded to Nuwakot, Rasuwa Morang and Jhapa
The expansion of the GSF program in Nepal aims to
support the Government of Nepal to achieve national sanitation target
of 100% coverage by taking up the most challenging 8 Terai districts
with low sanitation coverage. The campaign will follow the approach
as prescribed by the National Sanitation and Hygiene Master Plan.
Therefore, the campaign will be led by District Water Sanitation and
Hygiene Coordination Committee (D-WASHCCs), Village Development Committee
(VDC) Level Water Sanitation and Hygiene Coordination Committee
(V-WASH-CCs) and Municipal Level Water Sanitation and Hygiene
Coordination Committee (M-WASH-CC) with continuous and regular
monitoring and follow up by Regional Water and Sanitation Coordination
Committee (R-WASH-CCs ) and National Sanitation and Hygiene
Coordination Committee (NSHCC).UN-Habitat through its sub-grantees will
provide support, to the respective D-WASH-CC and V/M-WASH-CC based on
an agreed program of action for implementing the Master Plan.
PROGRAMME AREA
In the first phase of implementing GSF, six districts in
Nepal were selected by National Hygiene and Sanitation Coordination Committee
(NHSCC) covering all development regions as well as all ecological regions –
Mountain, Hill and Terai. GSF has targeted 205 Village Development Committees
(VDCs) and 6 municipalities from the 6 GSF program districts including an
additional municipality from Kailali district, Tikapur Municipality. The GSF
program districts are Arghakhanchi, Bajura, Bardiya, Bhaktapur, Sindhupalchowk
and Sunsari. Out of these 6 districts, Bajura, Bardiya, Arghakhanchi and
Bhaktapur and Tikapur municipality had attained ODF status. Sindhupalchowk had
reached 98% coverage before the earthquake with alarming setback after
earthquake. After the successful intervention in six districts as mentioned
above, GSF extended its program activities in 9 additional districts – Dolakha
(mountain region) and eight Terai districts in the eastern and central regions
of Nepal with low sanitation coverage (Parsa, Bara, Rautahat, Sarlahi,
Mahottari, Dhanusha, Siraha and Saptari). The program was further
extended to four districts which are Nuwakot, Rasuwa, Morang and Jhapa.At
present, the program is implemented in 485 VDCs of 13 districts for the ODF
campaign.
PROGRAMME COMPONENTS
a) Consensus Building
b) Sector Coordination and Planning
c) Capacity Building
d) ODF Campaign
e) Sanitation Marketing
f) Monitoring
g) Knowledge Management
GSF ENTITIES IN NEPAL
National Sanitation and Hygiene Coordination Committee
(NSHCC): NSHCC gives strategic guidance and supervision to the GSF program
in Nepal to ensure alignment with national sector policies, strategies, and the
Master Plan. NSHCC is a multi-stakeholder platform led by the government.
Executing Agency (EA): EA administers the fund,
including the award of grants in response to proposals, technical support to
Sub-grantees and monitoring.
Sub-grantees: Sub-grantees are the implementing agencies for
GSF program. Local bodies, NGOs and CBOs are eligible agencies to work as the
Sub-grantees
WORKING PRINCIPLE OF GSF PROGRAMME IN NEPAL
Policy enabler: Support for localizing Sanitation and
Hygiene Master Plan 2011.
Ownership and institutionalization: Integration and linkage with
government program through local level Strategic Plan/Plan of Action led by
local bodies.
Stakeholders Participation: Recognition of multi-stakeholders efforts in
central, regional, district, municipality and VDC levels
Campaign: Adoption of wider campaign approach to back up on going
sanitation movement.
Sustainability: Resource pooling, cost-sharing and local leaders






.jpg)
.jpg)



